
題目列表(包括答案和解析)
The most frightening words in the English language are, “Our computer is down.” You hear it more and more when you are on business. The other day I was at the airport waiting for a ticket to Washington and the girl in the ticket office said, “I’m sorry, I can’t sell you a ticket. Our computer is down.”
“If your computer is down, just write me out a ticket.”
“I can’t write you out a ticket. The computer is the only one allowed to do so.”
I looked down on the computer and every passenger was just standing there drinking coffee and staring at the black screen. Then I asked her, “What do all you people do?”
“We give the computer the information about your trip, and then it tells us whether you can fly with us or not.”
“So when it goes down, you go down with it.”
“That’s good, sir.”
“How long will the computer be down?” I wanted to know.
“I have no idea. Sometimes it’s down for 10 minutes, sometimes for two hours. There’s no way we can find out without asking the computer, and since it’s down it won’t answer us.”
After the girl told me they had no backup (備用) computer, I said. “Let’s forget the computer. What about your planes? They’re still flying, aren’t they?”
“I couldn’t tell without asking the computer.”
“Maybe I could just go to the gate and ask the pilot if he’s flying to Washington,” I suggested.
“I wouldn’t know what gate to send you to. Even if the pilot was going to Washington, he couldn’t take you if you didn’t have a ticket.”
“Is there any other airline flying to Washington within the next few hours?”
“I wouldn’t know,” she said, pointing at the dark screen. “Only ‘IT’ knows. ‘It’ can’t tell me.”
By this time there were quite a few people standing in lines. The word soon spread to other travelers that the computer was down. Some people went white, some people started to cry and still others kicked their luggage.
56. The best title for the article is ____________.
A. When the Computer Is Down B. The Most Frightening Words
C. The Computer of the Airport D. Asking the Computer
57. What could the girl in the ticket office do for the passengers without asking the computer?
A. She could sell a ticket.
B. She could write out a ticket.
C. She could answer the passengers’ questions.
D. She could do nothing.
58. Why didn’t they have a backup computer?
A. Because it was easy down
B. It isn’t mentioned.
C. Because it was not advanced enough.
D. Because it was not as big as the main computer.
59. The last paragraph suggests that ____________.
A. a modern computer won’t be down
B. computers can take the place of humans
C. sometimes a computer may bring suffering to people
D. there will be great changes in computers
60. What's the purpose of the author’s writing this story?
A. To state that nowadays people are too dependent on computers.
B. To blame the girl in the ticket office.
C. To inform passengers of the news.
D. To describe how the airport staff work.
Su Hua is studying at Cambridge, UK. She has bought a bicycle and is worried about security(安全). Her friend, Kate, found this article and sent it to her.
| Introduction A lot of crime is against bicycles. About 150,000 bicycles are stolen every year and most are never found. You can prevent this happening by following a few careful steps. Basic Security Do not leave your bicycle in out-of-the-way places. Always lock your bicycle when you leave. Secure it to lampposts or trees. Take off smaller parts and take them with you, for example lights and saddles(車座). Locks Get a good lock. There are many different types in the shops. Buy one that has been tested against attack. Ask for a recommendation from a bike shop. Marking Security marking your bike can act as a deterrent to a thief. It can also help the police find your bicycle. It should be clearly written and include your postcode and your house or flat number. This will provide a simple way to identify your bicycle. Registration There are a number of companies who will security mark your bicycle for you. They will then put your registration number and personal details on their computer database. Then if your bicycle is found it will be easy to contact you. Finally Keep a record of the bicycle yourself: its make, model and registration number. You can even take a photograph of it. This will prove the bicycle belongs to you. |
| A.Locks. | B.Marking. | C.Registration. | D.Basic Security. |
| A.help you recognize your bike |
| B.help the police find your bicycle |
| C.stop someone stealing your bicycle |
| D.stop you worrying about your bike |
| A.in the bike shop and your computer |
| B.in a police station and a security company |
| C.in a security company and your university |
| D.by yourself and in a security company |
| A.to tell you what to do if your bicycle is stolen |
| B.to suggest ways of keeping your bicycle safe |
| C.to give you advice on where to buy a good lock |
| D.to say why you shouldn’t keep your bicycle in a quiet place |
Su Hua is studying at Cambridge, UK.She has bought a bicycle and is worried about security (安全).Her friend, Kate, found this article and sent it to her.
Introduction
A lot of crime is against bicycles.About 150,000 bicycles are stolen every year and most are never found.You can prevent this happening by following a few careful steps.
Basic Security
Do not leave your bicycle in out-of-the-way places.Always lock your bicycle when you leave.
Secure it to lampposts or trees.Take off smaller parts and take them with you, for example lights and saddles ( 車座).
Locks
Get a good lock.There are many different types in the shops.Buy one that has been tested
against attack.Ask for a recommendation from a bike shop.
Marking
Security marking your bike can act as a deterrent to a thief.It can also help the police find your bicycle.It should be clearly written and include your postcode and your house or flat number.This will provide a simple way to identify your bicycle.
Registration
There are a number of companies who will security mark your bicycle for you.They will then put your registration number and personal details on their computer database.Then if your bicycle is found it will be easy to contact you.
Finally
Keep a record of the bicycle yourself: its make, model and registration number.You can even
take a photograph of it.This will prove the bicycle belongs to you.
1.Which part of the text gives you information on how to lock up your bicycle when you leave it?
A.Locks. B.Marking. C.Registration. D.Basic Security.
2.The underlined phrase “act as a deterrent to a thief” means ______.
A.help you recognize your bike B.help the police find your bicycle
C.stop someone stealing your bicycle D.stop you worrying about your bike
3.The article advises you to keep a record of your bicycle ______.
A.in the bike shop and your computer
B.in a police station and a security company
C.in a security company and your university
D.by yourself and in a security company
4.The main purpose of this article is ______.
A.to tell you what to do if your bicycle is stolen
B.to suggest ways of keeping your bicycle safe
C.to give you advice on where to buy a good lock
D.to say why you shouldn’t keep your bicycle in a quiet place
You may not pay much attention to your daily elevator ride. Many of us use a lift several times during the day without really thinking about it. But Lee Gray, PhD, of the University of North Carolina, US, has made it his business to examine this overlooked form of public transport. He is known as the “Elevator Guy”.
?? “The lift becomes this interesting social space where etiquette(禮儀)is sort of strange,” Gray told the BBC. “They are socially very interesting but often very awkward places.”
?? We walk in and usually turn around to face the door. If someone else comes in, we may have to move. And here, according to Gray, liftusers unthinkingly go through a set pattern of movements. He told the BBC what he had observed.
?? He explained that when you are the only one inside a lift, you can do whatever you want – it’s your own little box.
?? If there are two of you, you go into different corners, standing diagonally(對(duì)角線地)across from each other to create distance.
?? When a third person enters, you will unconsciously form a triangle. And when there is a fourth person it becomes a square, with someone in every corner. A fifth person is probably going to have to stand in the middle.
?? New entrants to the lift will need to size up the situation when the doors slide open and then act decisively. Once in, for most people the rule is simple – look down, or look at your phone.
?? Why are we so awkward in lifts?
?? “You don’t have enough space,” Professor Babette Renneberg, a clinical psychologist at the Free University of Berlin, told the BBC. “Usually when we meet other people we have about an arm’s length of distance between us. And that’s not possible in most elevators.”
?? In such a small, enclosed space it becomes very important to act in a way that cannot be construed(理解)as threatening or strange. “The easiest way to do this is to avoid eye contact,” she said.
1.The main purpose of the article is to _______.
A. share an interesting but awkward elevator ride
B. tell us some unwritten rules of elevator etiquette
C. analyze what makes people feel awkward in an elevator
B. remind us not to behave strangely when in an elevator
2.According to Gray, when people enter an elevator, they usually _______.
A. turn around and greet one another
B. look around or examine their phone
C. try to keep a distance from other people
D. make eye contact with those in the elevator
3. Which of the following describes how people usually stand when they are in the elevator?

4. The underlined phrase “size up” in Paragraph 7 is closest in meaning to _______.
A. judge??????? B. ignore????? C. put up with???? D. make the best of ????????????? ?????????????
You may not pay much attention to your daily elevator ride. Many of us use a lift several times during the day without really thinking about it. But Lee Gray, PhD, of the University of North Carolina, US, has made it his business to examine this overlooked form of public transport. He is known as the “Elevator Guy”.
“The lift becomes this interesting social space where etiquette (禮儀) is sort of odd (奇怪的),” Gray told the BBC. “They [elevators] are socially very interesting but often very awkward places.”
We walk in and usually turn around to face the door. If someone else comes in, we may have to move. And here, according to Gray, liftusers unthinkingly go through a set pattern of movements. He told the BBC what he had observed.
He explained that when you are the only one inside a lift, you can do whatever you want – it’s your own little box.
If there are two of you, you go into different corners, standing diagonally (對(duì)角線地) across from each other to create distance.
When a third person enters, you will unconsciously form a triangle. And when there is a fourth person it becomes a square, with someone in every corner. A fifth person is probably going to have to stand in the middle.
New entrants to the lift will need to size up the situation when the doors slide open and then act decisively. Once in, for most people the rule is simple – look down, or look at your phone.
Why are we so awkward in lifts?
“You don’t have enough space,” Professor Babette Renneberg, a clinical psychologist at the Free University of Berlin, told the BBC. “Usually when we meet other people we have about an arm’s length of distance between us. And that’s not possible in most elevators.”
In such a small, enclosed space it becomes very important to act in a way that cannot be construed (理解) as threatening or odd. “The easiest way to do this is to avoid eye contact,” she said.
1.The main purpose of the article is to _____.
A. remind us to enjoy ourselves in the elevator
B. tell us some unwritten rules of elevator etiquette
C. share an interesting but awkward elevator ride
D. analyze what makes people feel awkward in an elevator
2.According to Gray, when people enter an elevator, they usually _____.
A. turn around and greet one another
B. look around or examine their phone
C. make eye contact with those in the elevator
D. try to keep a distance from other people
3.Which of the following describes how people usually stand when there are at least two people in an elevator?
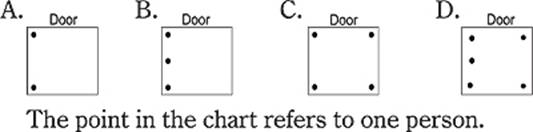
4.The underlined phrase “size up” in Paragraph 7 is closest in meaning to _____.
A. judge B. ignore C. put up with D. make the best of
5.According to the article, people feel awkward in lifts because of _____.
A. someone’s odd behaviors
B. the lack of space
C. their unfamiliarity with one another
D. their eye contact with one another
湖北省互聯(lián)網(wǎng)違法和不良信息舉報(bào)平臺(tái) | 網(wǎng)上有害信息舉報(bào)專區(qū) | 電信詐騙舉報(bào)專區(qū) | 涉歷史虛無主義有害信息舉報(bào)專區(qū) | 涉企侵權(quán)舉報(bào)專區(qū)
違法和不良信息舉報(bào)電話:027-86699610 舉報(bào)郵箱:58377363@163.com